
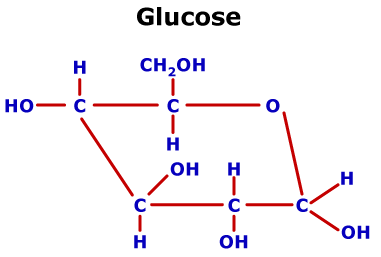
Specialized carbohydrates may be oxidized or have other chemical groups attached to the hydroxyls for specific functions. In order to form oligosaccharides or polysaccharides, the hydroxyl group attached to the anomeric carbon links to a specific carbon in the next saccharide. In this ring structure the hydrogen atom and hydroxyl group can be attached to the anomeric carbon in two different ways, forming two stereoisomers called alpha (ɑ) and beta (β) (Figure 1). The resulting hemiacetal or hemiketal connects the carbonyl carbon (called the anomeric carbon) to another carbon atom via an oxygen atom to form a 5- or 6-membered ring. The carbonyl carbon reacts with a hydroxyl group in the same molecule, four or five carbons away. Most biological monosaccharides form closed ring structures. These carbon atoms are linked to each other in a chain and have hydrogen atoms, hydroxyls, ketones, or aldehyde groups attached to them. This is why learning about the compositions and shapes of glycans can help us understand the functions of these molecules.Ĭommon monosaccharides contain either five carbons (pentoses like ribose) or six carbon atoms (hexoses like glucose). Although glycans are an important class of biological macromolecules, they can link to other macromolecules such as proteins and lipids to enhance their properties and functions. Unlike protein, where amino acids are linearly linked via standard peptide bonds, the bonds linking monosaccharides can be at different locations, allowing glycans to form branched chains with unique shapes and functions.

While proteins are made of building blocks called amino acids, glycans are composed of sugar units or "monosaccharides" (such as glucose and fructose), linked together through specific bonds to form "oligosaccharides" (such as sucrose and lactose, comprised of a few monosaccharides) and "polysaccharides" (such as starch and cellulose, comprised of many monosaccharides). Glycans have specific 3D shapes and functions in biology. Sugars are part of a family of chemicals called "carbohydrates." Although the terms "sugar" and "carbohydrate" are often used interchangeably in many discussions, glycobiologists who study the structure, biosynthesis, and functions of carbohydrates prefer to use more specific terms such as saccharides (for sugars) and glycans for their polymers. Historically, small molecules such as glucose, fructose, and sucrose have been collectively called "sugars." Chemical research has shown that these molecules are composed of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen with the typical formula of (CH 2O) n. Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, and Access.Exploring the Structural Biology of Bioenergy.Exploring the Structural Biology of Cancer.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
